Skin cancers
Signs of skin cancers
Overview
There is types of skin cancers that develops more often on skin exposed to the sun, some other types are independent of sun exposure, and they can develop anywhere.
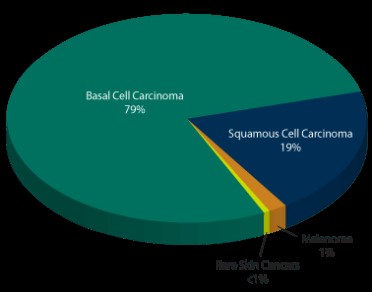
The most common types are:
- basal cell carcinoma
- squamous cell carcinoma
- melanoma
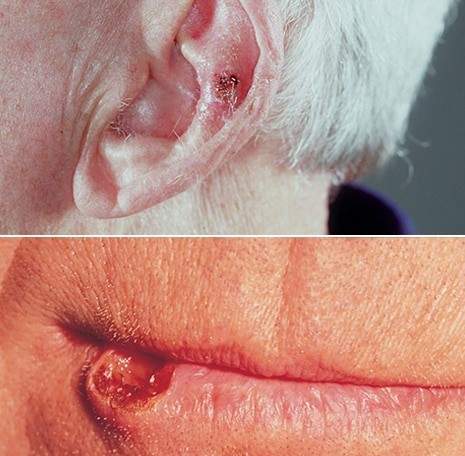
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the skinSymptoms
Where skin cancer develops
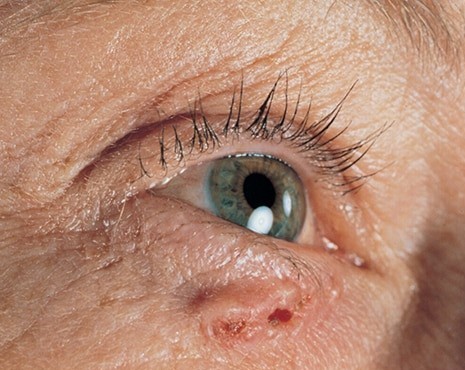
Basal cell carcinoma signs and symptoms
The most common and luckily the least aggressive of the skin cancers, it very rarely metastasize .It has local agressivity and grows slowly.
Basal cell carcinoma occurs in sun-exposed areas more often , such as your neck or face.
Basal cell carcinoma may appear as:
- A pearly or waxy bump
- A flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion
- A bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and returns
BCC nodular type
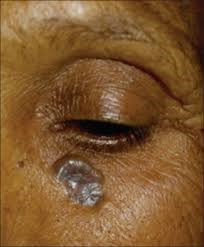
BCC pigmented type
BCC Morpheaform type
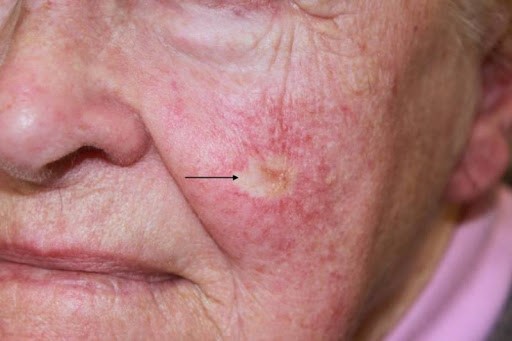
Squamous cell carcinoma signs and symptoms
The second most common, more aggressive than BCC, it has more tendency to spread to regional lymph nodes (first filter), it rarely gives distant metastasis.
Most often, squamous cell carcinoma occurs on sun-exposed areas of the face, ears and hands, however in dark skin people this is not always the case.
Squamous cell carcinoma may appear as:
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A firm, red nodule ulcerated in the middle that doesn’t heal
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
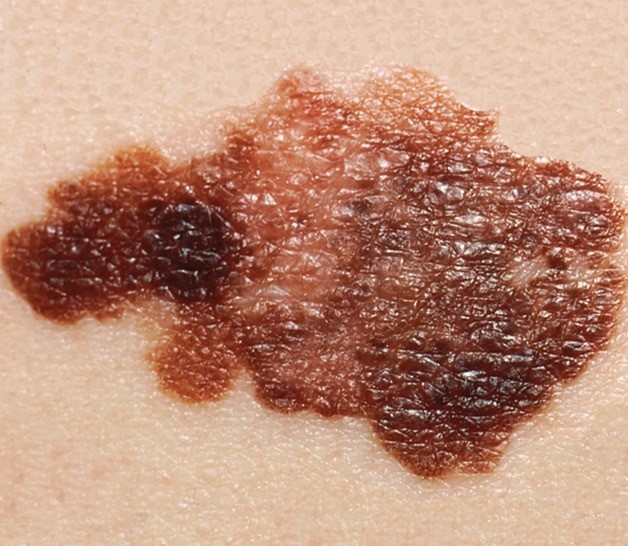
Melanoma skin cancer symptoms and signs
Melanoma can develop anywhere on your body, in otherwise normal skin or in an existing mole that becomes cancerous. Melanoma most often appears on the face or the trunk of affected men. In women, this type of cancer most often develops on the lower legs. In both men and women, melanoma can occur on skin that hasn’t been exposed to the sun.
Melanoma skin cancer can affect people of any skin tone. In people with darker skin tones, melanoma tends to occur on the palms or soles, or under the fingernails or toenails.
Melanoma skin cancer signs include:
- A new large brownish spot with darker speckles
- A mole that changes in color, size or feel or that bleeds
- A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black
- A painful lesion that itches or burns
- Dark lesions on your palms , soles , fingertips or toes , or on mucousa lining your mouth, nose, vagina or anus
SSM Melanoma
Other, less common types of skin cancer include:
- Kaposi sarcoma.
Kaposi sarcoma mainly occurs in people with weakened immune systems, such as people with AIDS, and in people who had undergone organ transplants and taking immunosupressors.
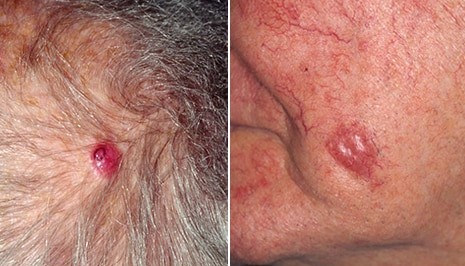
- Merkel cell carcinoma.Merkel cell carcinoma causes firm, shiny. Merkel cell carcinoma is most often found on the head, neck and trunk.
Merkel cell carcinoma
- Sebaceous gland carcinoma.This uncommon and aggressive cancer originates in the oil glands in the skin. Sebaceous gland carcinomas
Causes
Ultraviolet light and other potential causes
Much of the damage to DNA in skin cells results from ultraviolet (UV) radiation found in sunlight and in the lights used in tanning beds. But sun exposure doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of skin cancer include:
- Fair skin.
- Excessive sun exposure and sunburns.
- Sunny or high-altitude climates.
- Precancerous skin lesions. Having skin lesions known as actinic keratoses
- A family history of skin cancer..
- A personal history of skin cancer.
- A weakened immune system.
- Exposure to radiation..
- Exposure to certain substances.Exposure to certain substances, such as arsenic, may increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Some genetic skin condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum
Prevention
Most skin cancers are preventable. To protect yourself, follow these skin cancer prevention tips:
- Avoid the sun during the middle of the day
.
- Wear sunscreen year-round.
- Wear protective clothing.Sunscreens don’t provide complete protection from UV rays. So cover your skin with dark, tightly woven clothing that covers your arms and legs, and a broad-brimmed hat, which provides more protection than a baseball cap or visor does.
Some companies also sell photoprotective clothing. A dermatologist can recommend an appropriate brand.
Don’t forget sunglasses. Look for those that block both types of UV radiation — UVA and UVB rays.
- Avoid tanning beds.Lights used in tanning beds emit UV rays and can increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Be aware of sun-sensitizing medications.Some common prescription and over-the-counter drugs, including antibiotics, can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist about the side effects of any medications you take. If they increase your sensitivity to sunlight, take extra precautions to stay out of the sun in order to protect your skin.
- Check your skin regularly and report changes to your